Introduction
Goal feel the big picture of computer networks
keywords Internet, protocol, network edge, network core, performance, protocol layers, service models.
HW : what ISP is servicing GIST college?
Internet : nut and bolt view
Network = Edge devices + core + links
Edge devices All devices we usually use.
Core Packet switches, routers .. ISP : Internet service providers ex. KT, SKT, LG U+
Links There are different structures of communication links (optic fiber, copper, radio ..) links between switches
Network All of these(Edge devices, core, links) make of the whole network All these networks are connected by ISP
Internet is a network of networks. Interconnected ISPs
Protocols Every rules between devices are written in RFC(Request for comments). IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force) writes RFCs.
Internet : service-wise view
What services are built upon internet? Web, streaming video, email, social media, cloud computing ...
Internet provides programming interface(background) between distributed devices.
What is a protocol?
Protocols define the format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt
Network Edge
hosts : clients and servers caution. servers are also at the edge of a network.
Access networks
network that connects edge hosts to the networks
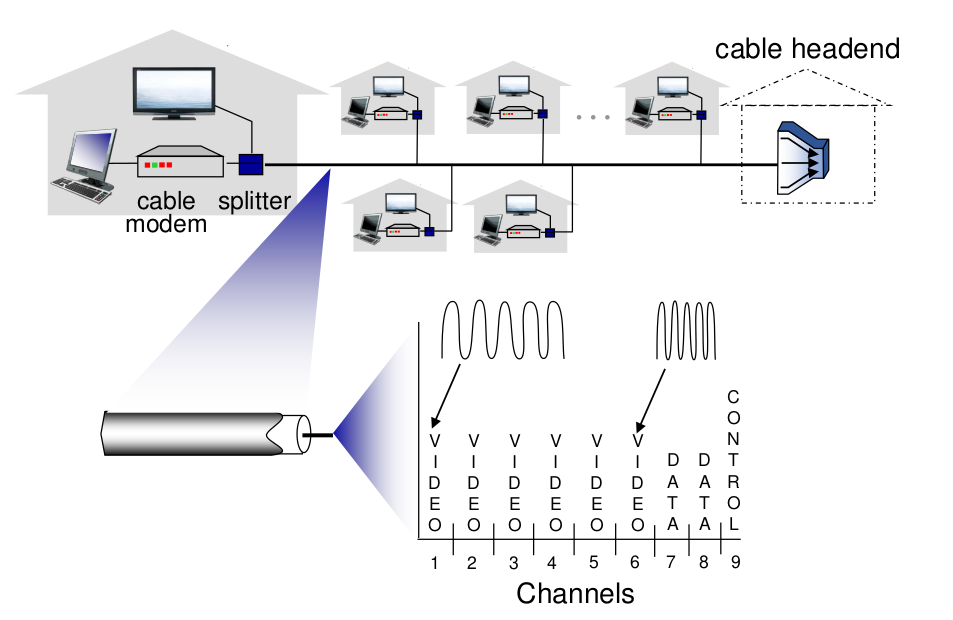
cable-based access
-
this access networks work based on FDM(Frequency division multiplexing) #todo : What is FDM? #todo: What is multiplexing? A way of sharing one channel between services. we divide by frequency, time slot, or others..
-
They use HFC(hybrid fiber coax) for linking. Asymmetric in downstream/upstream transmission rate
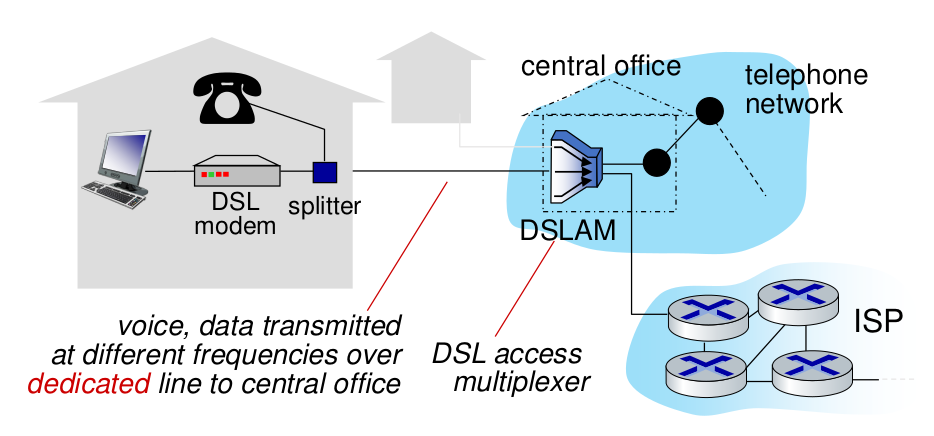
digital subscriber line(DSL)
This DSLAM works upon the existing landline telephones infrastructure.
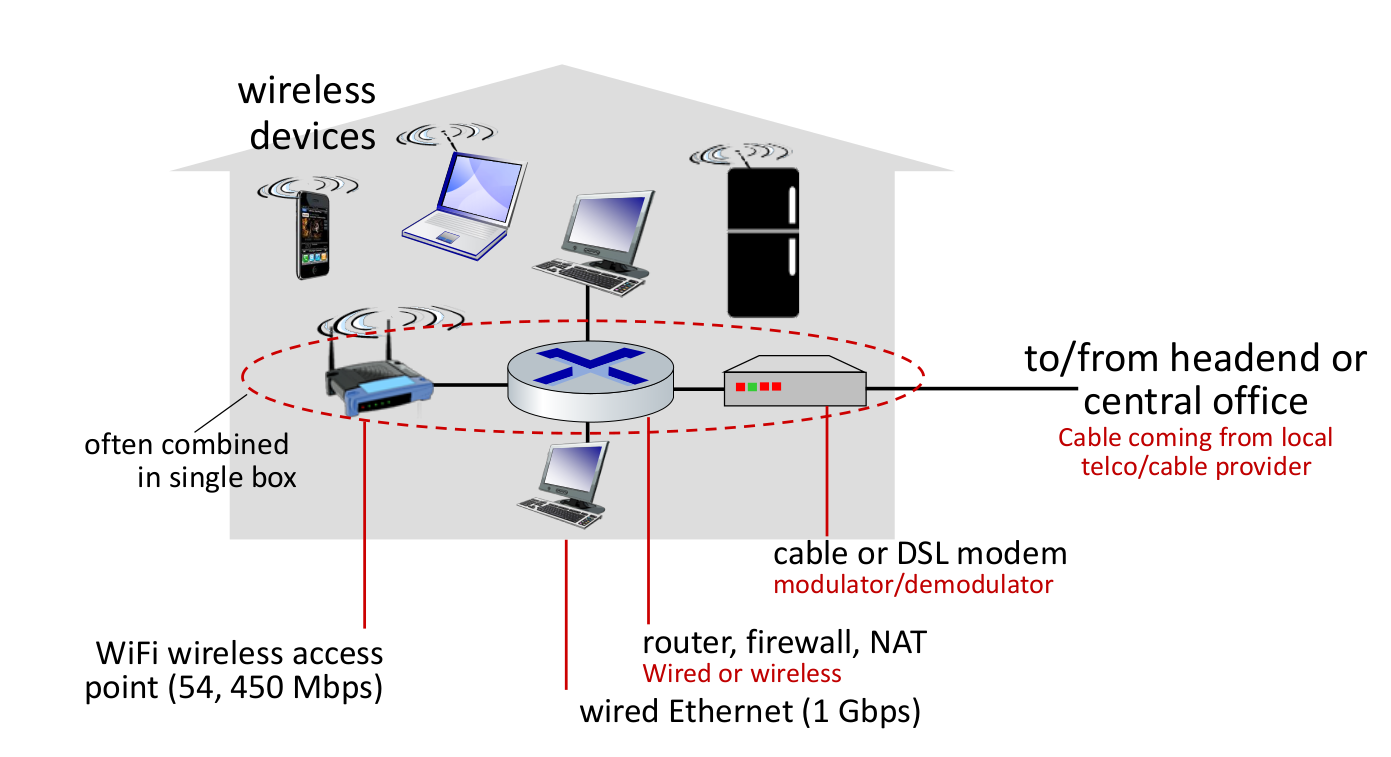
Home networks
Central office is a commonly used term.
Enterprise Networks
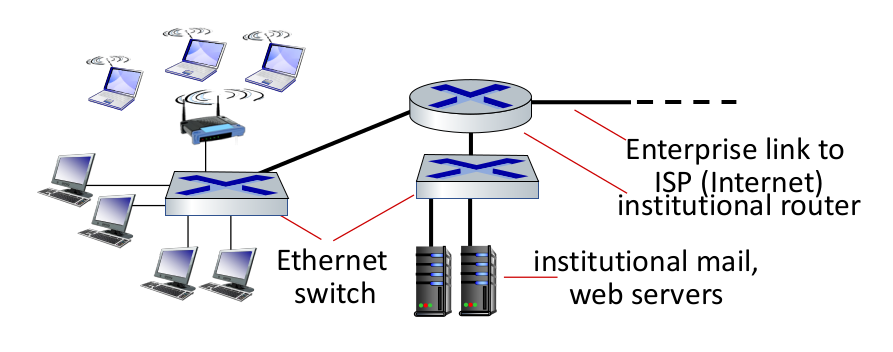 Mix of wired, wireless networks.
Mix of wired, wireless networks.
data center networks
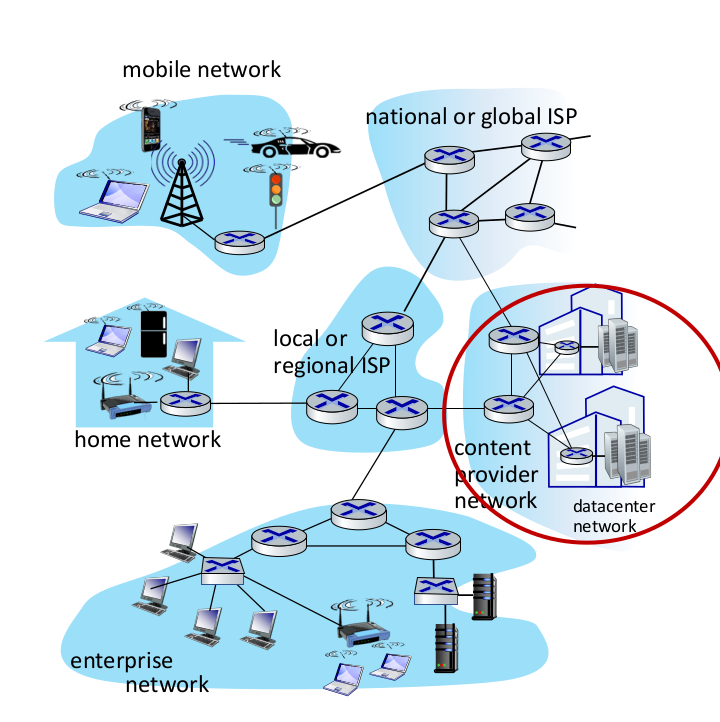 Supported by high bandwidth for more availability
often merged with a CDN. A company that needs big size data center buys CDN and build themselves.
Supported by high bandwidth for more availability
often merged with a CDN. A company that needs big size data center buys CDN and build themselves.
Transmission taking time
- sent target is divided into chunks, (usually called packets)
- Let each chunks have size $L$ bits.
- chunks are sent through link.
- Each links have their own transmission rate $R$.
- $$(packet: transmission: delay) = time:need:to:transmit:L-bit:chunk = L/R$$
Links : physical media
Twisted pairs (TP) Coaxial Cable, Fiber optic cables, ...
Links : wireless media
frequency division is made by the goverment, or on RFC.
Network Core
Core is made of interconnected routers. The routers make up packet-switching network.
The network forwards packets from source to destination.
The main task of routers Routing : to find the path Forwarding: forward the packet that way
The information of destinations are padded inside the packet. Routers build forwarding tables through an routing algorithm, and according to it router forwards the packet.
Packet switching : store-and-forward
#todo : transmission delay, end-end delay
Packet switching : queue
There exists a queueing delay. If the queue storage is full, it commits packet drop
![[../images/20230831140901.png]] #todo: write about throughput, packet drop rate.
Circuit Switching
used mainly in telephone networks.
make a call setup. it takes a certain amount of time. the line is reserved for my call. we use the line solely for my call.
benefits guaranteed performance. (no other interference)
How do links perform multiplexing? FDM: I use 100MHz bandwidth, you use 200MHz bandwith TDM : Me first, you next. ![[../images/20230831141647.png]]