Introduction
Summary
keywords
TODO
HW
Exercise*
Next time
IP
IP datagram
TTL : prevent looping. (not usually occurs because network is hierarchical) type of service
Overheads
- 20 bytes of IP header,
- 20 bytes of TCP header.
IP fragmentation
Network links have max transfer size (MTU) IP fragmentation can occur at any router IP assembly always happen only at the last router.
3 fields on header 16 identifier, flags, offset fragflag 0 indicates the last fragment. fragmentation was about the flow capacity. offset - size
where fragmentation happens? depended on the size?
IP addressing
32 bit identifier with each host or router interface IP address is associated with an interface, not a device.
router also has interface. #test: prefix matching problems
- virtual network interfaces By default, 192.168.56.1 is the IP address assigned for Ethernet adapter to virtual box.
There's Layer 2 device (called hub) on blue areas
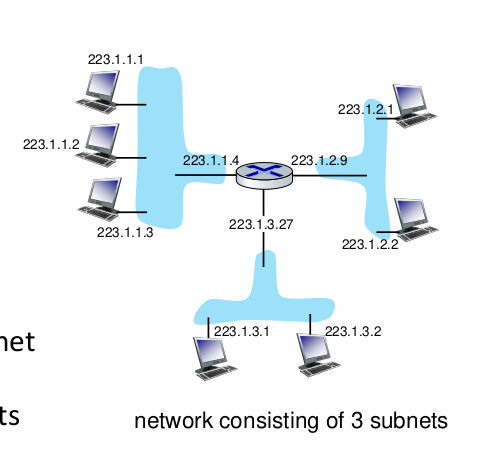
subnets
223.1.1.X, 223.1.3.X,223.1.2.X is a subnet address part.
subnet is indicated by subnet mask. one device can be in several subnet, each adapter to each subnet.
for 223.1.3.0/24, /24 part means 24 bits in front are for subnet address.
CIDR (Classless InterDomain Routing)
subnet portion can be of arbitrary length
a.b.c.d/x
How do you get IP address?
-
How does host get their IP?
- Option 1) Hard Coded in config file
- Option 2) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(DHCP)
-
How does network get their IP?
- gets allocated portion of its provider ISP's address space
DHCP
It is a Application layer protocol. Goal
-
can renew its lease(time duration of borrowing) on address in use
-
allows reuse of address.
-
support for mobile users who join/leave network.
-
discover, offer, request, ack
DHCP scenario
-
There's a DHCP server connected in the network.
-
DHCP broadcast : broadcast send to
255.255.255.0:67IP.- src:0.0.0.0,68
- dest:255.255.255.0,67
- yladdr: 0.0.0.0
- transaction ID:654
-
DHCP server serves at port 67.
-
DHCP Offer : How about
<address on yladdr>this IP?- src:223.1.2.5,67
- dest:255.255.255.0,68
- yladdr: 223.1.2.4
- transaction ID:654
- lifetime: 3600 secs
-
destination is till broadcasting.
-
The client recognizes the offer by transaction
-
there is a lifetime
-
DHCP request : OK, can I use it?
- src:0.0.0.0,68
- dest:255.255.255.255,67
- yladdr: 223.2.3.4
- transaction ID:654
- lifetime: 3600 secs
-
DHCP Ack : yes, you can
-
- src:.0.0.0,68
- dest:255.255.255.0,67
- yladdr: 0.0.0.0
- transaction ID:654
- asdfaf?
-
normal mobile device only uses request, ack. They only use their address saved in client device. They only confirms if the
DHCP sends more info other than IP.
- first-hop router
- local DNS server IP
- network mask
How does network get subnet part of IP?
- ISP bought a portion of address space. ex. 11001000 00010111 00010000 00000000
- ISP divides them into subnets into however they like. ex. 11001000 00010111 00010010 00000000/23 ex. 11001000 00010111 00010020 00000000/23
This way, IP is a natural Hierarchical Addressing Space.