Introduction
Summary
keywords
TODO
HW
Exercise*
Next time
Gray code
The codes are sequenced so as the adjacent code has only one bit difference.

Why do we need concept of gray codes?
- To detect how many bits are corrupted in the data.
- When the data is changed, the value difference is equal to the number of corrupted bits.
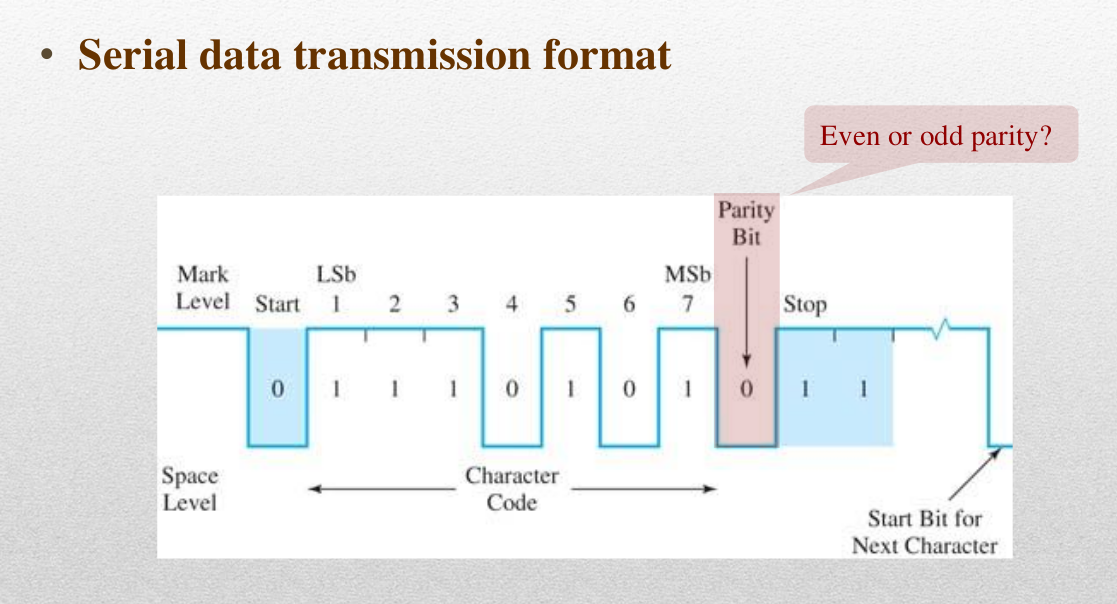
Error Detection Codes
- Parity bits
- It adjusts so that the number f 1s in a group to be even(even parity) or odd(odd parity)
- It cannot correctly detect multiple bit errors.
- It cannot fix errors.
Serial Data Bit representation
Boolean Algebra
Diagrams, truth table, and function.
-
The dot symbol stands for 'not' operation; the triangle symbol stands for 'buffer' operation. Combined, it means 'not' operation.
-
truth table is the only definitive way to express operation.
-
truth table uses "HIGH", "LOW", "X" as the entity(Due to the underlying hardware tech).
-
X means either Low or high logic level: Don't care condition
-
not is typographically expressed in prime or overbar.
-
overbar is a complement expression.
useful two-binary-variable operations
-
AND $F(x_1,x_2) = x_1 x_2$
-
OR $F(x_1,x_2) = x_1+x_2$
-
XOR (OR, but not both) $F(x_1,x_2) = x_1⊕x_2$
-
NAND
-
NOR
-
E-XOR
-
NAND, NOR has duality
-
All the other operations can be implemented with NAND and NOR gates; it is universal.
Logic Circuits
There are canonical form or others. Canonical form definitively expresses truth tables.
Basic Axioms of Boolean Algebra
- only concerns three operations only (AND, OR, Complement)